News/All pieces
Save the date: RRR2021 conference

On renewable resources from wet and rewetted peatlands
28/05/2020 In the light of the Paris Agreement and the necessity to reduce all anthropogenic CO2 emissions globally to net zero around the year 2050, peatland rewetting and innovative land use concepts for wet peatlands are an important contribution to achieve the goal. Thus, the GMC hosts the 3rd International Conference on the Utilisation of Wetland Plants, the RRR2021 - Renewable Resources from Wet and Rewetted Peatlands from 9th-11th March2021 in Greifswald. It includes an international conference, excursions, as well as technical exhibitions. We invite you to submit an abstract for oral or poster presentation until September 15th 2020. Abstract submission will open in August. Note of acceptance will be given until October 31st 2020. If a presence event is not possible due to Corona restrictions, the conference will be held in a digital format. See www.rrr2021.com for conference details and subscribe via info@rrr2021.com for conference updates.
Estonian president visiting

EUKI project informs about peatland utilisation and its role in agricultural and climate policy
22/05/2020 On May the 21st the Estonian president Kersti Kaljulaid visited peatland restoration sites in Estonia. At this occasion the Estonian Nature Fund, partner in the EUKI - project “Paludiculture in the Baltic States”, handed over a merged document of an Estonian translation of the GMC position paper on Peatlands and the EU CAP after 2020 and the Paludiculture Policy Brief that was compiled within in the EUKI project. Kersti Kaljulaid pleaded for the rewetting of abandoned peat mining sites for carbon storage and restoration of valuable habitats for peatland species.
Peatlands in the education

Suggestions for business game, excursion and peatland flat
04/05/2020 Only what you know you can protect. That is why it is so important to explain to even the youngest children what peatlands are and what importance they have. In her master's thesis Peatlands in the Education for Sustainable Development in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania at the University of Greifswald, Tabea Feldmann conducted a status quo analysis. Using the example of the peatland Mannhagener Moor near Greifswald, she demonstrated the possibilities of implementation and showed how peatlands can be taken into account in school curricula. The peatland case developed by her offers numerous suggestions to bring children, families, pupils and adults closer to peatlands. Since knowledge transfer and education about peatlands is an important concern of the Greifswald Mire Centre, it now makes the material available as part of its proceedings (in German).
New map of peatlands in Germany
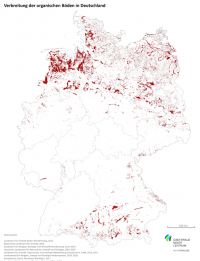
Now for download in the Proceedings of the GMC
04/05/2020 The Greifswald Mire Centre compiled an up-to-date map on the current distribution of peatlands in Germany. The Aggregated Map of Organic Soils in Germany is also freely available as a GIS data download. It’s area-specific data can now be used, for example, to plan trans-federal climate and nature conservation measures in peatlands. The Greifswald Mire Centre developed the map with help of responsible administrative institutions of the individual federal states within the MoorDialog project. It was published as the first volume of the Proceedings of the Greifswald Mire Centre in 2020 (in German).
Postponing rewetting will warm climate for centuries
GMC-scientists warn in nature communications
02/04/2020 The positive climate effects of peatland rewetting are determined by the long-term avoidance of carbon dioxide, not by the emission of methane. A research team from the Universities of Rostock and Greifswald shows this in the article Prompt rewetting of drained peatlands reduces climate warming despite methane emissions in the scientific journal nature communications. According to the scientists rapid action is therefore needed to promptly rewet global peatlands. The longer this is postponed, the greater the climate damage.
The team of the WETSCAPES project comes to this conclusion by analysing the worldwide unique data collection on peatland area and land use of the Global Peatland Database of the Greifswald Mire Centre. The scientists investigated the effects of various land use scenarios in a simulation analysis. They calculated the quantity and climate impact of the individual greenhouse gases emitted into the atmosphere in annual steps up to the year 2100.
Peatlands and CAP
New position paper to keep digital contact
24/03/2020 Instead of meeting Members of European Parliament today – one of the many events cancelled due to the current Corona pandemic – GMC together with many partners distributed a new position paper on peatlands and the EU’s Common Agricultural Policy (CAP). The main target is to facilitate the new environmental ambitions of the Post-2020 Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) and to create coherence between agricultural and climate policies by safeguarding and stimulating the preservation of carbon-rich soils through protection of peatlands. The paper summarises current knowledge and lists solutions and recommendations, and has been compiled together with more than 20 research institutions and NGOs from across the EU. The event in European Parliament, which was to be hosted by MEP Peter Jahr and MEP Michal Wiezik and organised jointly by the Greifswald Mire Centre (GMC), the Interdisciplinary Research Centre for Baltic Sea Region Studies (IFZO), the National University of Ireland Galway and Wetlands International, can be hopefully held later this year.
Paludi + Design
Workshop by GMC and Art University Halle
01/03/2020 Braiding cattail leaves, felting seed hair, cooking peat moss - at the end of February, 15 art and design students at Burg Giebichenstein University of Art and Design Halle (die BURG) experimented with material from paludiculture plants. Small baskets, innovative seating and new fabrics were created in this first workshop in cooperation between the Greifswald Mire Centre and the Burg Giebichenstein University of Art and Design Halle. The sustainable raw materials are interesting for the designers since they have not been explored in art so far. At the same time the materials meet their standards of climate friendliness. The GMC values this cooperation as an opportunity for new ideas with chic and well-reviewed manufacturing chains for paludicultural products. In an accompanying public lecture, the GMC gave an introduction to the diverse world of peatlands, especially rewetted areas, and the use of paludiculture biomass.


World Wetlands Day 2020

3 x peatland participation and experience
02/02/2020 On the occasion of the World Wetlands Day (WWD), the Greifswald Moor Centrum offered three times “Join in and Experience” around peatlands on Saturday, February 1st, 2020. This gave people in the region the opportunity to find out more about peatlands and to help preserve them.
Around 30 volunteers lent a hand in the hands-on campaign in Mannhagener Moor between Greifswald and Stralsund on Saturday, February 1st. The task was to cut and remove wood to create habitat for cotton grass, sundew or the rare mother-of-pearl butterfly. The hands-on activities in Mannhagener Moor, an area under the responsibility of the Succow Foundation, help to develop the moor again into an intact biotope.
On the same day, the Succow Foundation invited visitors to the Karrendorfer Wiesen for a free tour of around three hours. Along the embankment, around 40 visitors could observe thousands of herons and mountain ducks on Lake Kooser, first groups of iron ducks on the island of Koos or geese on the salt grassland. The traveling exhibition "Moor, climate protection and paludiculture" of the Greifswald Moor Centrum was officially opened on February 1st in the chalk hall of the Königsstuhl National Park Center. It explains why intact peatlands are climate savers and how they can be used sustainably, and can be seen there until the end of March.
Peatlands at COP25

Summary: Topic set, huge need for action
13/12/2019 On 13th December the UNFCCC Conference in Madrid came to an end after tough negotiations. The summary of the peatland and climate team of the Greifswald Mire Centre on site: Unsatisfactory to sobering. The topics of peatland and climate protection, restoration and sustainable use were more present than ever before in the conference's supporting programme. On the opening day, the GMC had organized a side event "Mapping, Monitoring and Climate-Friendly Management of Peatlands" together with the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), the Japanese Agency for International Cooperation (JICA) and the Global Environmental Centre (GEC) from Malaysia. On 4th December, a theme day in the Indonesian country pavilion focused on climate-friendly peatland management, especially in tropical latitudes. On 5th December, the Global Peatlands Initiative, of which the GMC is a founding member, presented itself in the German national pavilion. Internationally, politicians as well as representatives of NGOs see wet and rewetted peatlands as an efficient nature-based solution for climate protection and adaptation to climate change.
GMC funding granted
NUE supports our work from Greifswald to Brussels
07/12/2019 For the next two years, the Norddeutsche Stiftung für Umwelt und Entwicklung (NUE) is supporting the development of the Greifswald Mire Centre. Scientific expertise on peatland is to be transferred to voluntary organisations and politics. The GMC leaders Dr. Franziska Tanneberger and Greta Gaudig recently spoke with Vorpommern farmers and nature conservationists, Chancellor Angela Merkel and EU parliamentarians about the potentials of moor climate protection. As a "generational change" is ongoing, NUE will support the partners in the GMC to strengthe capacity and maintain the GMC as a successful and thriving partnership. The University of Greifswald, partner in the GMC, will set up the first permanent professorship for peatland sciences in Germany in 2020 with the support of the state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and the Stifterverband der deutschen Wissenschaft.